Article verified for Release 15.1 on September 28, 2025.
This article provides candidates with clear, step-by-step guidance on how to use the integrated calculator feature during a test. For instructions on how to enable this feature for test takers, refer to this article.
Accessing the Calculator
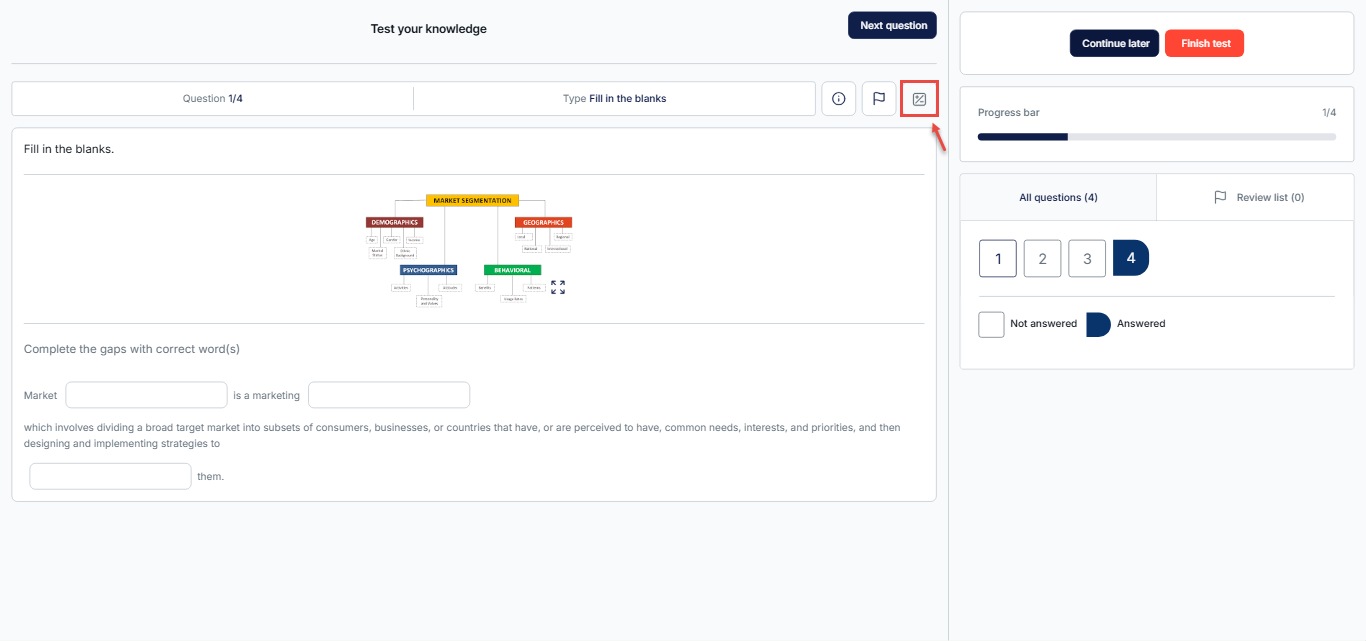
During the test, click the calculator icon located beneath the exam title to open it.
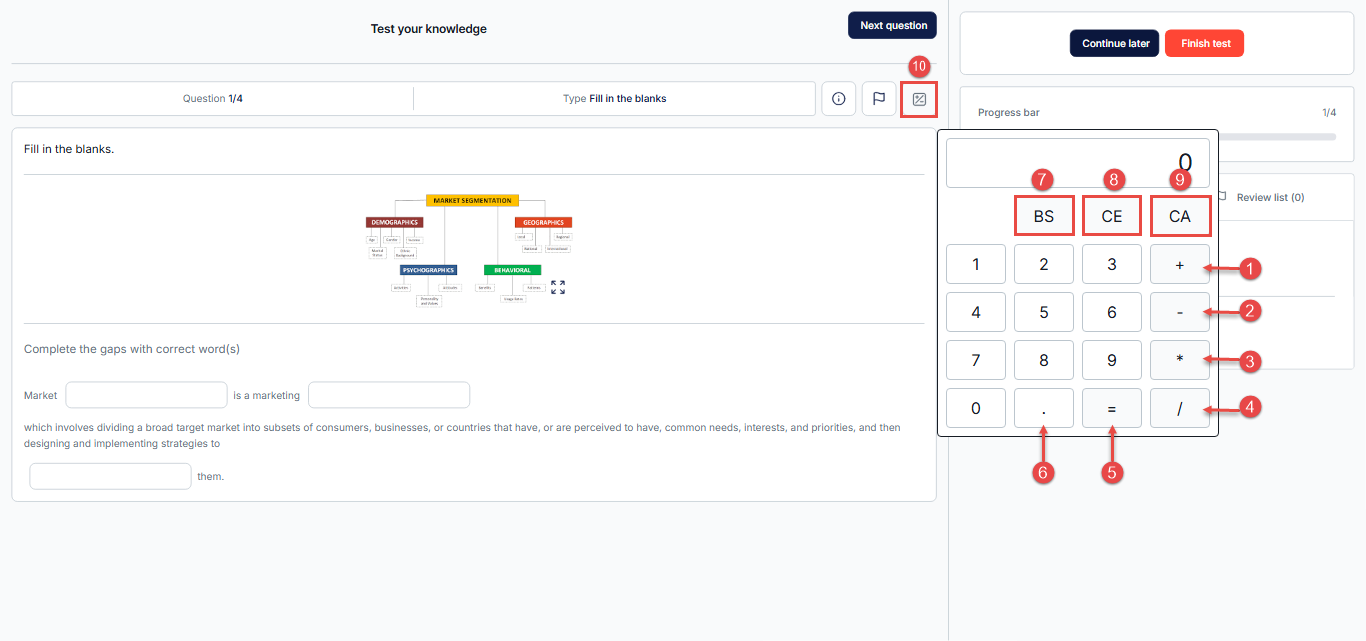
Using the Basic Calculator
- + (Addition): Adds two numbers together to calculate the sum.
- – (Subtraction): Subtracts the second number from the first.
- * (Multiplication): Multiplies two numbers together.
- / (Division): Divides the first number by the second.
- = (Equals): Calculates and displays the result of the current operation or expression.
- Decimal point (.): Allows you to enter decimal numbers. For example, to enter “3.14,” press 3, then the decimal point, then 1, 4
- BS (Backspace): Removes the last digit or character entered. Useful for correcting small mistakes without clearing the entire input.
- CE (Clear Entry): Clears the current entry but does not erase the entire calculation. For example, if you entered the wrong number but still want to continue with the calculation, this button clears only that number.
- CA (Clear All): Resets everything, including the display and ongoing calculation. Use this if you want to start from scratch.
- Closing the Calculator: To close the calculator, simply click the calculator icon again. This will hide the calculator from your screen.
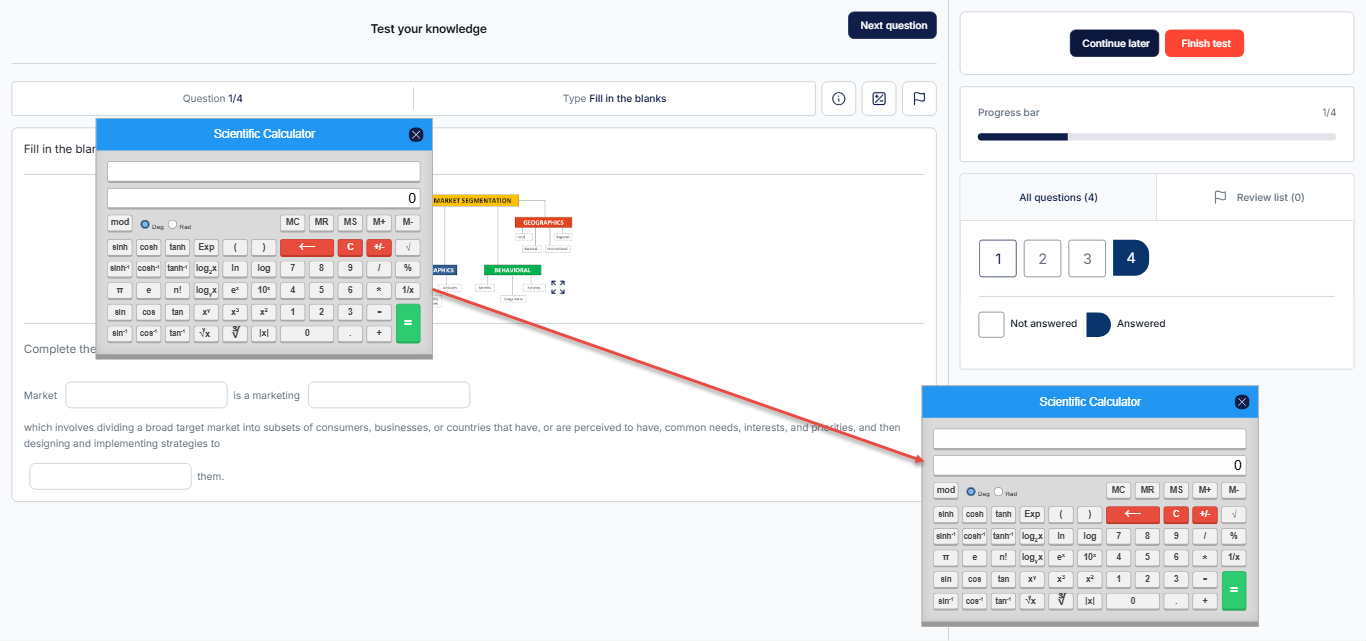
Using the Scientific Calculator
You can use your mouse to drag and reposition the calculator anywhere within the exam tab for your convenience.
You can operate the calculator by clicking the buttons provided on the screen with your mouse.
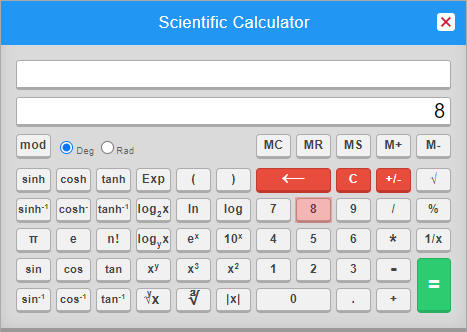
- Backspace (←): Enter ← Deletes the last digit entered in the input box
- Clear all the inputs (C): Clears all current inputs.
- Percent Operator (%): To calculate 30 percent of 400, enter “30“, “%“, “400“, “=“.
- Reciprocal (1/x): To calculate 1/175, enter “175“, “1/x” , “=“.
- Arithmetic Operators (+, – , * , /): Use “*” to multiply, “/” to divide, “+” to add, and “–” to subtract.
- Memory Keys (MC, MR, MS, M+, M-):
-
-
- MC is used to clear the memory.
- MS is used to store the number in memory.
- MR is used to read the number from memory.
- M+ is used to add the memory to the number available on display, then stored in memory.
- M- is used to subtract the number on display from the memory value, and then store it in memory.
-
- Unary plus and Minus (+/-): To calculate -4 * 3, enter “4“, “+/-“, “*“, “3“, “=“.
- Power Roots (√ , ∛ ,y√x): To calculate √5, press “5” and then key “√x“. To calculate 2√5, press “5“, “y√x“, and then “2“.
- Logarithmic functions (log, ln, log2x, logyX): To calculate log(30), enter “30” and press the “log” button. To calculate log2(30), enter “30“, then “logyX“, and press “2“.
- Trigonometric Operations: To find sin(50), enter “50” first and then the “sin” function from the calculator.
Good practices:
-
-
-
Press C before starting a new calculation to clear previous inputs.
-
Use parentheses and brackets to group operations and ensure accurate results, especially with complex expressions.
-
-
Bad practices:
-
-
-
Performing multiple operations in a single line without using parentheses can lead to incorrect results.
-
Leaving parentheses unbalanced can cause calculation errors.
-
Changing the angle unit (Deg or Rad) in the middle of a calculation may lead to incorrect trigonometric results.
-
-